Smart sanctions, also known as targeted sanctions, are restrictions applied to specific individuals, entities, sectors, or activities rather than entire countries. They are designed to maximize pressure on those responsible for illicit activity while minimizing harm to innocent populations.
For financial institutions, smart sanctions create new compliance challenges. Unlike blanket embargoes, they require more sophisticated screening processes to ensure that transactions involving designated persons or sectors are identified and blocked.
Smart Sanctions
Smart sanctions are a form of economic sanction that focuses on precision. Instead of prohibiting all business with a country, they target actors such as government officials, corporations, financial institutions, or industries linked to corruption, terrorism, or human rights abuses.
For example, the European Union often issues smart (targeted) sanctions against individuals or entities connected to conflict zones, including asset freezes, travel bans, and prohibitions on providing financial or economic resources.
Similarly, the United Nations, through its Security Council sanctions committees, applies such measures in regimes related to armed conflict, terrorism and conflict prevention
This targeted approach reduces unintended humanitarian consequences while maintaining strong political and economic pressure.
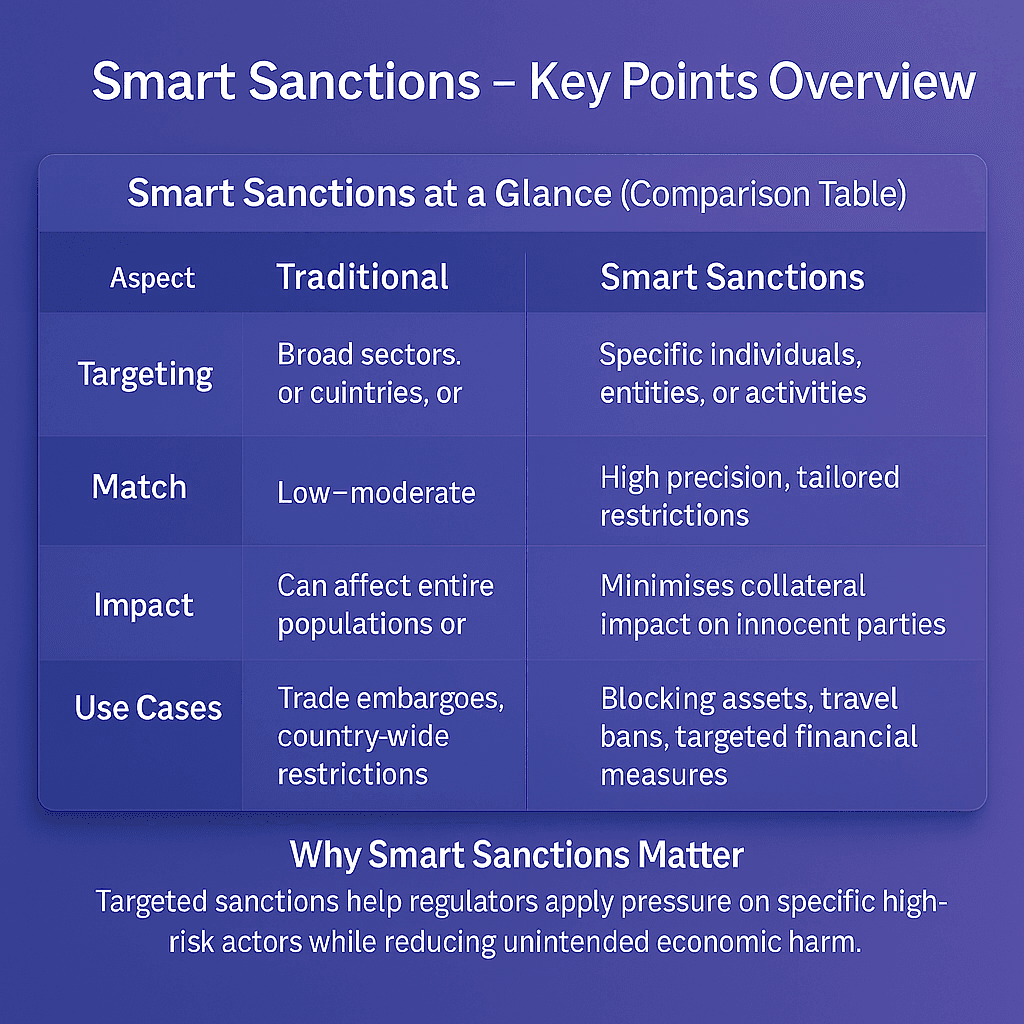
Why Smart Sanctions Matter In AML Compliance
Smart sanctions directly impact AML compliance because they require enhanced Watchlist Management and Customer Screening capabilities. Institutions must detect not only named individuals but also entities indirectly owned or controlled by sanctioned parties.
The United Nations Security Council (UNSC) emphasises that targeted sanctions are critical tools in counterterrorism and conflict prevention, employing measures like travel bans, asset freezes and arms embargoes against individuals and entities responsible for destabilising behaviour.
Similarly, the European Commission confirms that EU restrictive measures are precisely directed at persons and entities deemed responsible for objectionable conduct, and requires accurate identification and monitoring of such listed individuals or organisations to enforce sanctions effectively
Without strong compliance systems, financial institutions risk facilitating prohibited transactions, leading to fines and reputational damage.
Key Types Of Smart Sanctions
Smart sanctions can take multiple forms depending on the objectives of the sanctioning body:
Asset Freezes: Prohibiting access to or control of funds belonging to designated persons.
Travel Bans: Restricting the movement of individuals subject to sanctions.
Sectoral Sanctions: Limiting financial services, trade, or investment in specific industries such as energy, defence, or technology.
Arms Embargoes: Blocking the sale or transfer of weapons to targeted entities.
Each of these requires institutions to maintain real-time screening and monitoring systems to remain compliant.
Regulatory Expectations For Smart Sanctions
Regulators expect financial institutions to implement systems that can accurately detect transactions linked to targeted sanctions.
This includes:
Maintaining up-to-date sanction lists from authorities like the OFAC, EU, and UNSC.
Identifying ownership structures where sanctioned individuals hold indirect stakes.
Screening payments in real time to prevent sanctioned transactions.
Applying enhanced due diligence to high-risk jurisdictions and sectors.
The U.S. Department of the Treasury has indicated that violations of targeted (smart) sanctions may result in being cut off from vital U.S. financial infrastructure or markets. For example, recent sanctions regimes have explicitly barred certain Russian financial institutions from access to U.S. dollar-based systems
The Future Of Smart Sanctions
Smart sanctions are expected to expand as governments seek more precise tools to influence behavior. Advances in graph analytics and network-based detection will help institutions identify complex ownership structures that conceal sanctioned parties.
Future frameworks may also incorporate AI-driven monitoring to reduce false positives, while regulators are likely to demand more transparency in how compliance systems apply sanctions rules. Institutions that invest in advanced Payment Screening and Transaction Monitoring will be best positioned to manage evolving obligations.
Strengthen Your Smart Sanctions Compliance Framework
Smart sanctions demand precise compliance strategies that balance risk detection with operational efficiency. Financial institutions must adapt their systems to keep pace with evolving sanctions regimes.
Contact Us Today To Strengthen Your AML Compliance Framework


