Suspicious Transaction Reports (STRs) are official reports filed by financial institutions to regulators when a transaction appears unusual, inconsistent with a customer’s profile, or potentially linked to money laundering or terrorist financing. STRs are a cornerstone of anti-money laundering (AML) frameworks, ensuring regulators can investigate and act on financial crime risks.
Suspicious Transaction Reports (STRs)
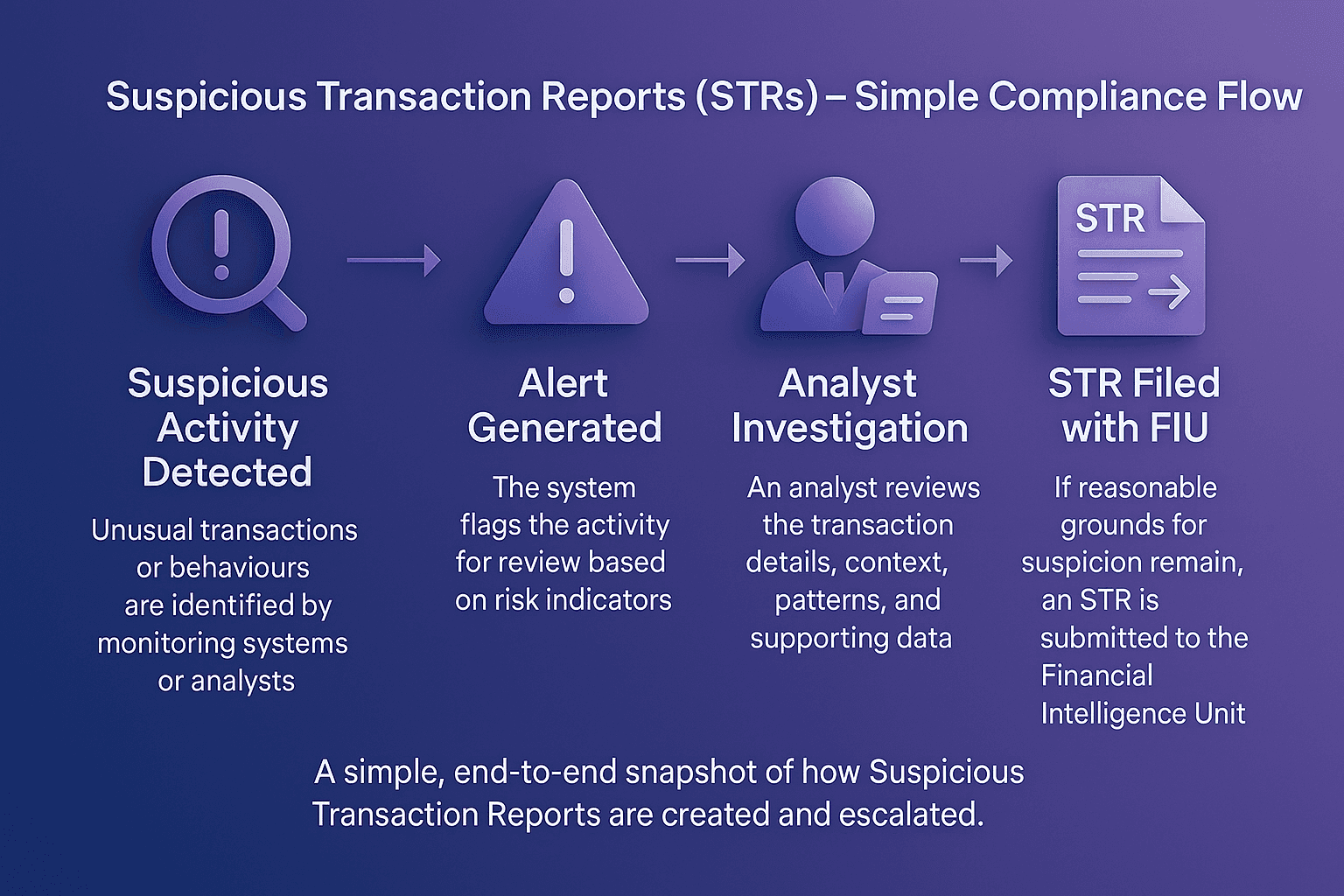
An STR is a formal report submitted by a financial institution or designated entity when it has reasonable grounds to suspect that a transaction may involve illicit activity. Unlike routine regulatory filings, STRs focus specifically on suspicious or abnormal transactions that cannot be readily explained by legitimate business purposes.
The filing requirements are established by international standards, including FATF, and adapted into national laws. For example, in the UK, under Part 7 of the Proceeds of Crime Act 2002 and the Money Laundering Regulations 2017, financial institutions and other regulated entities must file Suspicious Activity Reports (SARs) to the National Crime Agency (NCA) when they have knowledge or reasonable suspicion of money laundering.
In the US, under the Bank Secrecy Act, financial institutions must submit SARs to the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) whenever they detect suspicious activity.
Why STRs Matter In AML Compliance
Suspicious Transaction Reports are a critical part of AML compliance because they provide regulators with the intelligence needed to investigate and disrupt criminal networks.
Timely and accurate STR filings can prevent illicit funds from being integrated into the financial system.
Regulatory requirement: STRs are legally mandated, and failure to file can result in severe penalties.
Early detection of crime: STRs help regulators and law enforcement identify money laundering, terrorist financing, and fraud at an early stage.
Risk-based compliance: STRs often arise from monitoring systems such as Transaction Monitoring, which flag unusual activity for escalation.
Operational assurance: A robust Alert Adjudication process ensures suspicious alerts are investigated properly before STRs are filed.
Core Elements Of An STR
Filing an STR requires institutions to capture detailed information about the suspicious transaction. This ensures regulators have the necessary context for further investigation.
Transaction Details
The nature, amount, and timing of the transaction must be recorded, along with any unusual patterns observed.
Customer Information
Details about the customer, including identification data and account history, provide regulators with context on whether the activity aligns with their known profile.
Suspicion Indicators
The reasons why the transaction is considered suspicious must be documented clearly, including red flags such as structuring, inconsistent account activity, or links to high-risk jurisdictions.
The Future Of STRs In AML Compliance
The future of STRs lies in greater automation, improved data quality, and international cooperation. Regulators are increasingly focused on ensuring that STRs are not just numerous but also meaningful. Over-reporting of low-quality STRs can overwhelm regulators, while under-reporting undermines enforcement.
Technological advancements, including AI-powered monitoring and network analysis, are improving the precision of STR generation.
Regulators are also encouraging greater consistency in how STRs are reported across different countries. In the European Union, the European Commission’s new AML Regulation introduces a “Single Rulebook” for AML/CFT, which will apply directly to all Member States. Part of this framework includes plans for harmonised reporting formats and a standard STR template, to be developed by the new European Anti-Money Laundering Authority (AMLA).
Going forward, institutions that invest in data-driven compliance systems will be better positioned to meet STR obligations efficiently and effectively.
Strengthen Your STR Compliance Framework
Meeting STR obligations requires strong detection, escalation, and reporting processes. Institutions that streamline their monitoring and adjudication workflows are better equipped to file timely and accurate STRs.
Facctum’s Alert Adjudication solution ensures that suspicious alerts are properly reviewed and escalated, helping institutions meet STR requirements with confidence.
Contact Us Today To Strengthen Your AML Compliance Framework


