Watchlist management and name screening are two critical controls in anti-money laundering (AML) and sanctions compliance. While often discussed separately, they are most effective when integrated. Watchlist management ensures data quality and governance, while name screening applies that data to detect potential sanctions or politically exposed person (PEP) matches. Together, they create a continuous cycle of accuracy, transparency, and operational efficiency.
What Is Watchlist Management?
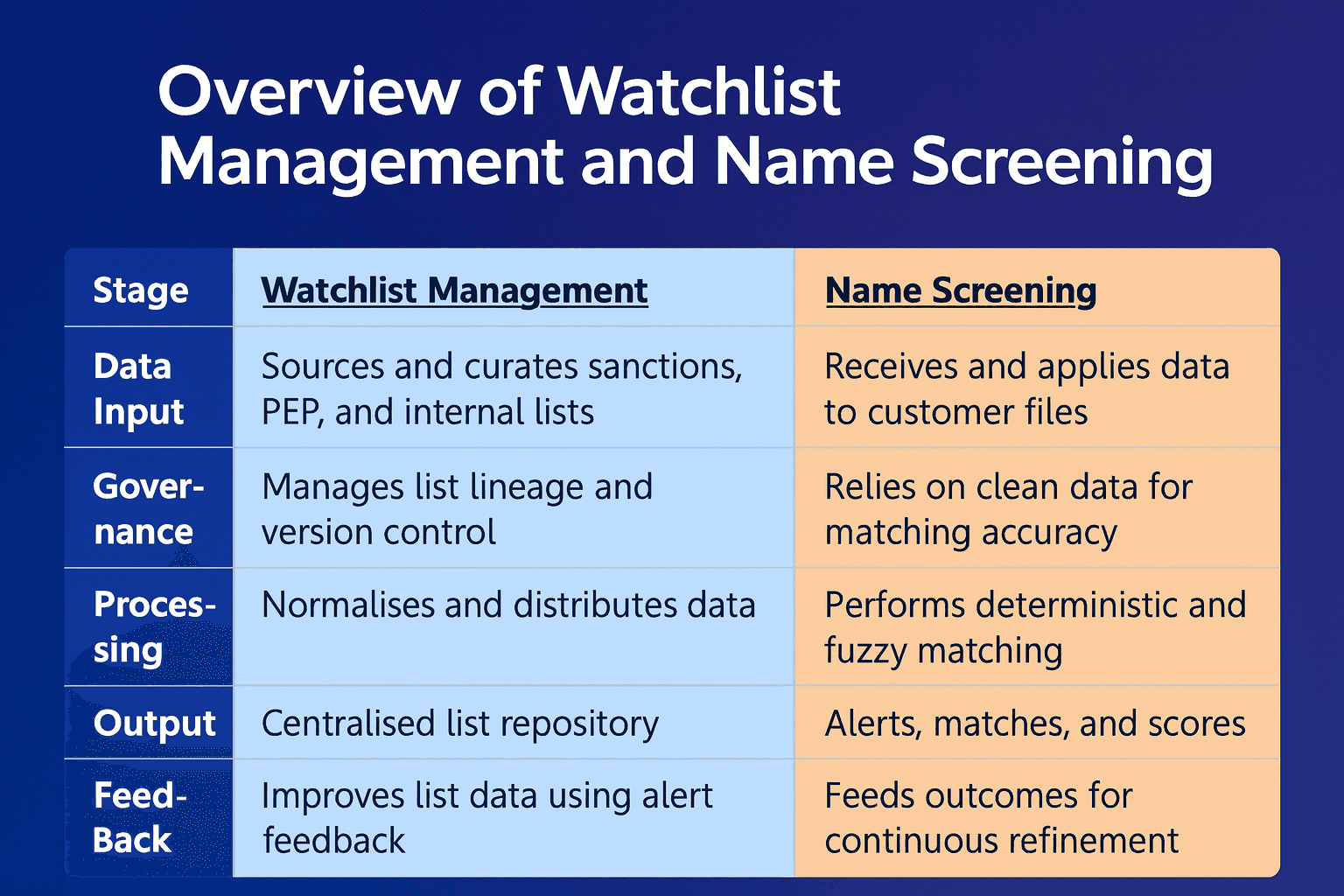
Watchlist management refers to the process of curating, maintaining, and distributing regulatory, sanctions, and PEP lists across compliance systems. It ensures that every screening engine uses a unified, up-to-date data source. This includes deduplication, version control, and audit tracking.
Platforms such as watchlist management handle these responsibilities, ensuring that lists from sources like OFAC, UN, and EU are consistently accurate and traceable. Poorly maintained watchlists can create data fragmentation and increase false positives in downstream screening processes.
Watchlist Management Benefits
Improved Data Integrity: Reduces duplication and outdated entries for cleaner screening results.
Faster Updates: Automates ingestion from regulators and removes manual refresh cycles.
Audit Readiness: Maintains lineage and change logs for every list version.
Cross-System Consistency: Ensures a single source of truth across multiple screening engines.
Strong list governance provides the foundation for effective detection and regulatory compliance.
What Is Name Screening?
Name screening is the process of comparing customer, counterparty, and transactional data against sanctioned entities, PEPs, and other restricted lists. It leverages exact, phonetic, transliteration, and fuzzy-matching techniques to detect high-risk relationships.
Solutions like customer screening automate this process, using AI-driven algorithms to reduce false positives and enhance explainability. Effective name screening depends on clean, governed data from watchlist management.
Name Screening Benefits
Enhanced Detection: Identifies potential matches across languages and data formats.
Fewer False Positives: Uses AI-driven matching and risk thresholds to optimise precision.
Regulatory Confidence: Delivers transparent match explanations for audits.
Real-Time Decisions: Enables instant risk detection during onboarding or payment processing.
Screening outcomes are only as strong as the list data they use, highlighting the importance of integration.
How Watchlist Management and Name Screening Work Together
When integrated, watchlist management feeds clean, structured lists directly into the screening engine. Screening systems then process customer data, generate alerts, and feed insights back into list governance. This creates a feedback loop that continuously improves accuracy.
This feedback cycle creates an adaptive compliance framework that strengthens both governance and detection.
Alert Adjudication and Continuous Improvement
Once alerts are generated, analysts must determine whether they represent genuine risk. This process, known as alert adjudication, closes the loop between screening and list governance. Adjudication outcomes help refine thresholds, reduce noise, and enhance list data quality.
Each resolved case contributes to institutional learning, allowing compliance teams to adapt faster to evolving regulatory demands and complex financial crime patterns.
Why Integration Improves Compliance Efficiency
By uniting watchlist management and name screening, financial institutions benefit from:
Consistent, governed data across all compliance layers.
Faster, explainable decision-making during onboarding and transactions.
Reduced false positives and improved analyst productivity.
Stronger regulatory alignment and defensible audit trails.
This integrated approach transforms compliance from a reactive control to a proactive intelligence system, ensuring long-term resilience and accuracy.
Implementation Best Practices
To maximise value from integration, teams should:
Automate data synchronisation between list management and screening.
Implement explainable algorithms for transparency.
Align with FATF Recommendations and the IMF AML-CFT framework for governance best practice.
Use alert outcomes to iteratively refine thresholds and lists.
When executed correctly, the synergy between both systems forms the backbone of a scalable, risk-based compliance programme.
FAQs About How Watchlist Management And Name Screening Work Together In Compliance




