In anti-money laundering (AML) programmes, watchlist data and screening data are the two pillars that determine the effectiveness of sanctions and risk detection controls. While watchlist data provides the foundation through curated regulatory and internal lists, screening data represents the transactional or customer information being compared against those lists. Understanding how they differ and interact is essential for maintaining compliance accuracy and operational speed.
Quick Summary
Watchlist data and screening data are interdependent components of every AML control framework. Watchlist data defines who or what must be screened, while screening data defines who or what is being screened.
Watchlist data: Curated and version-controlled datasets sourced from regulators such as OFAC, EU, and UN.
Screening data: Dynamic customer or transaction datasets used for matching and identifying potential risks.
Both must be accurate, consistent, and synchronised to deliver reliable compliance outcomes.
Watchlist Data Definition
Watchlist data refers to the authoritative sources of sanctioned or high-risk individuals, entities, or vessels. These datasets are updated frequently and distributed through governed systems like watchlist management. They include sanctions lists, politically exposed person (PEP) data, and adverse media records.
High-quality watchlist data ensures consistent coverage across all compliance systems, preventing missed matches and redundant alerts. Each list should be governed with metadata, lineage, and audit trails to support defensible reporting and adherence to supervisory frameworks such as the FATF Recommendations.
Screening Data Definition
Screening data represents the customer or transactional information that’s compared to watchlist data. It includes identifying attributes such as names, addresses, dates of birth, account numbers, and transaction metadata. Solutions like customer screening use this data to detect potential sanctions or PEP matches in real time.
For screening data to be effective, it must be complete, standardised, and regularly validated. Poor-quality data leads to false positives, delayed alerts, and increased manual workloads. Data management controls help ensure that screening inputs maintain accuracy and structure across systems.
Key Differences
Although both are essential for compliance, they serve distinct roles. Watchlist data represents who to look for, while screening data represents who you have. The table below summarises the key contrasts.
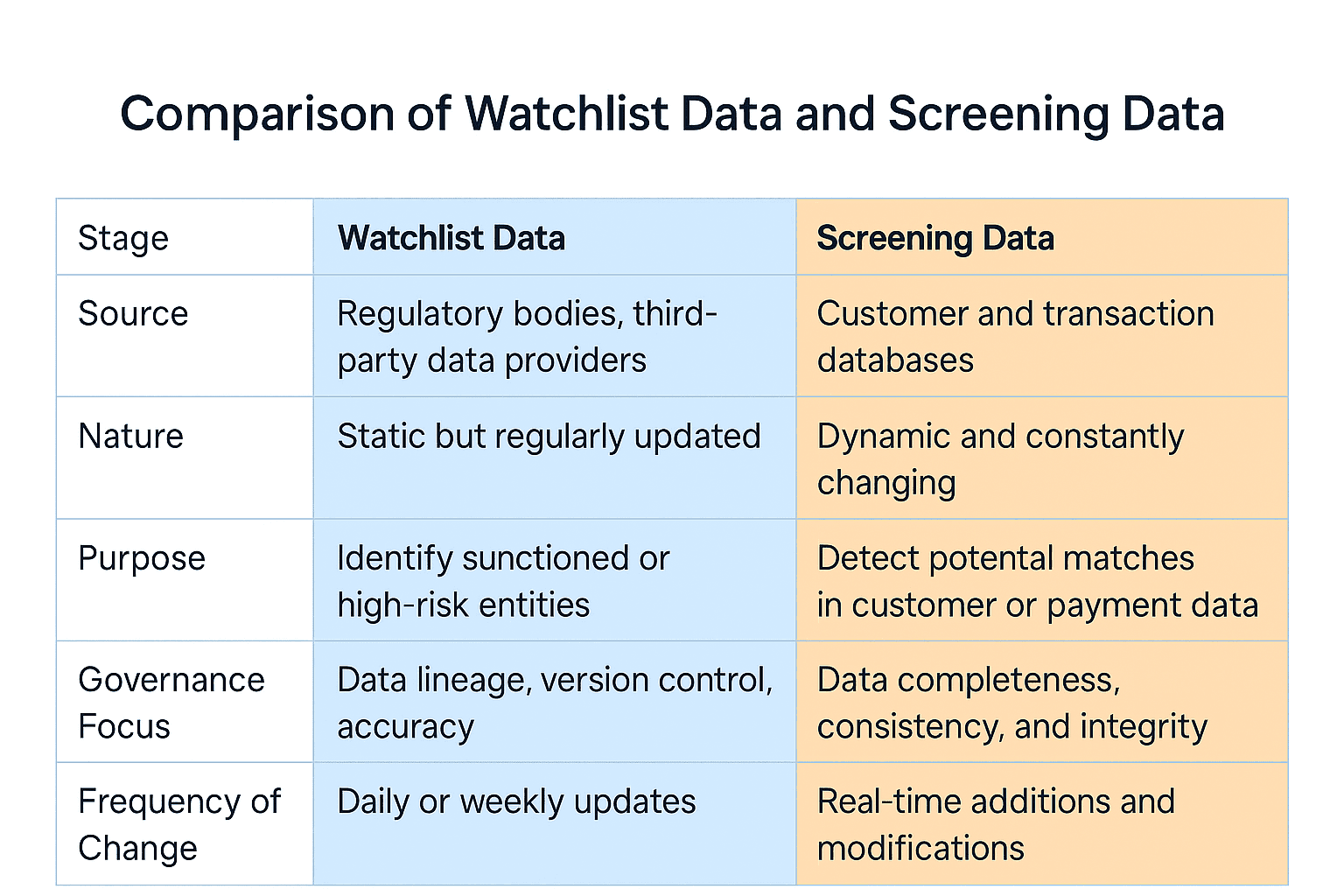
By aligning both data streams under a unified governance model, compliance teams reduce the risk of mismatched updates or inconsistent outcomes.
Benefits of High-Quality Watchlist Data
Strong governance over watchlist data delivers major operational and regulatory advantages:
Accurate, deduplicated datasets improve match precision
Simplified regulatory reporting through lineage and audit trails
Faster propagation of updates across multiple screening engines
Maintaining structured, transparent list data within watchlist management ensures a reliable foundation for downstream processes.
Benefits of Clean Screening Data
High-quality screening data enhances detection accuracy and improves analyst efficiency:
Reduced false positives through structured input formats
More accurate fuzzy matching and AI-driven scoring
Greater explainability in match outcomes
Solutions like customer screening rely on clean, well-structured data to enable defensible match results aligned with regulatory expectations.
How Watchlist Data and Screening Data Work Together
The two datasets operate in tandem: watchlist data defines the universe of risk, while screening data provides the input for evaluation. This relationship forms the foundation of every screening operation.
When a match occurs, results flow back into the watchlist and screening governance cycle. These insights support threshold tuning and list refinement, often resolved through alert adjudication. Continuous feedback ensures both data sets evolve in quality and accuracy.
Data Governance and Integration
Integration between watchlist and screening data is key to maintaining control. Platforms like payment screening and transaction monitoring depend on this synchronisation to make real-time risk decisions.
To achieve this alignment:
Define clear ownership and refresh schedules for both data types.
Establish APIs that automate updates between list and screening systems.
Ensure that changes to data schemas or formats are logged and validated before deployment.
Proper governance prevents drift, improves explainability, and enables consistency across systems.
External Regulatory Context
Regulators such as the IMF and OFSI emphasise that effective sanctions compliance depends on both accurate source data and precise matching. Supervisory reviews often examine how institutions govern and align these datasets to minimise operational and reputational risk.
Summary
Watchlist data and screening data may serve different roles, but both are essential for complete AML compliance. When properly governed and integrated, they enable real-time, reliable, and explainable risk detection that satisfies both regulators and internal stakeholders.




