Customer screening and transaction screening are two critical layers of anti-money laundering (AML) compliance. While both identify potential financial crime risks, they operate at different points in the customer and payment lifecycle. Understanding their roles, differences, and combined impact helps compliance teams design more effective, real-time control frameworks.
Quick Summary
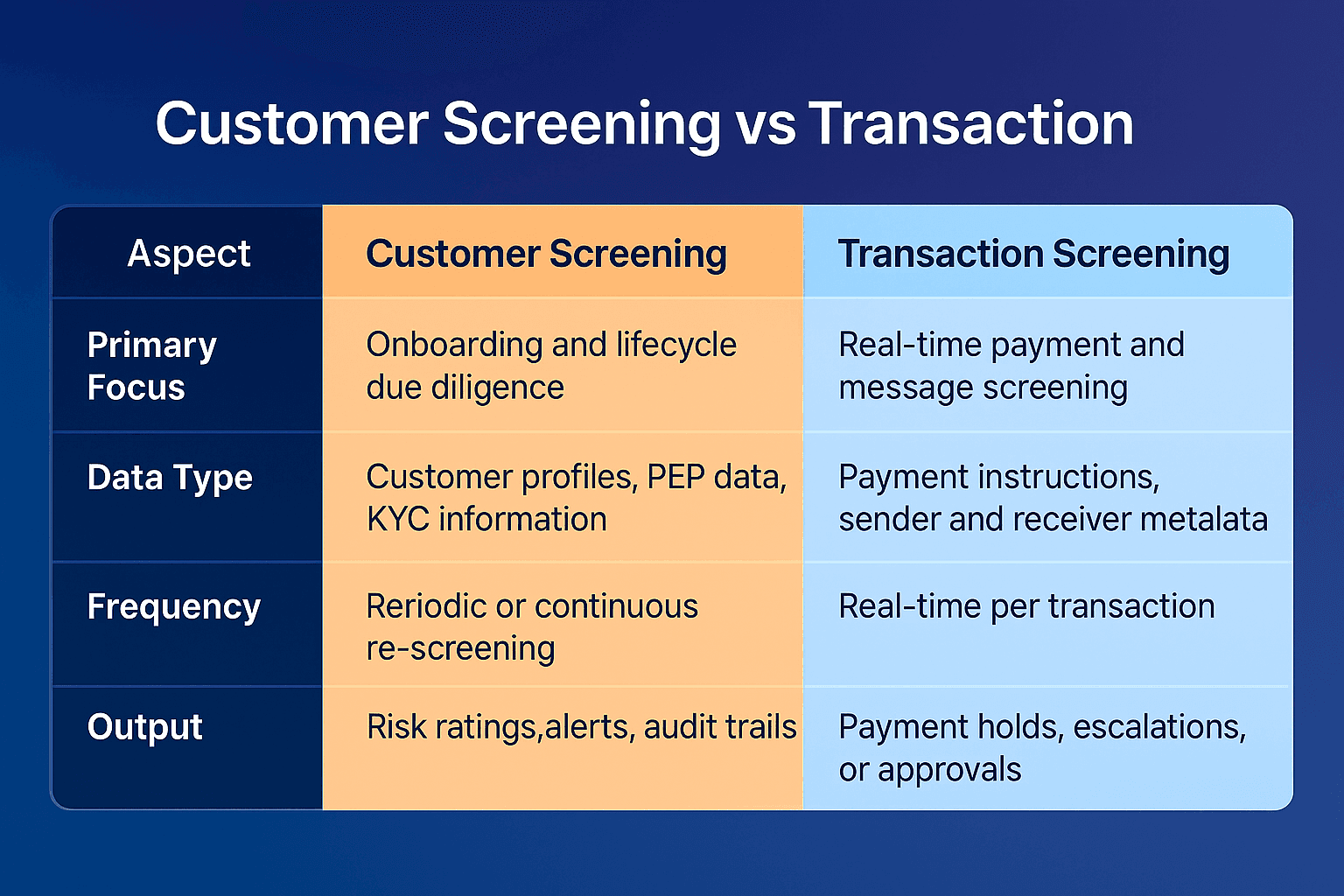
Customer screening: Evaluates individuals and entities at onboarding or during periodic reviews, comparing their information against sanctions, PEP, and adverse media lists.
Transaction screening: Analyses payments and message data in real time to detect sanctioned or suspicious transactions before processing.
Together, they deliver a multi-layered compliance approach that protects both customer integrity and payment safety.
What Is Customer Screening?
Customer screening is the process of verifying customer profiles against sanctions, politically exposed persons (PEP), and adverse media data. It typically occurs during onboarding and throughout the customer lifecycle.
Core components include:
Data Matching: Uses deterministic and fuzzy logic to identify potential matches.
Ongoing Monitoring: Automatically re-screens customers when watchlists or risk data change.
Explainable AI: Provides transparent rationale for each alert to support audits and regulator requests.
Batch or Real-Time Screening: Integrates with onboarding systems for fast approvals and minimal disruption.
Benefits of Customer Screening
Effective customer screening strengthens the onboarding process by ensuring each customer is accurately assessed before an account or service is approved. It helps institutions verify identities, detect sanctions or PEP risks early, and maintain a smoother, more transparent compliance workflow.
These advantages translate into faster decisions, fewer unnecessary alerts, and greater confidence in customer-level risk controls;
Fewer False Positives: Improved matching algorithms reduce unnecessary alerts.
Faster Onboarding: Enables real-time verification with minimal manual review.
Regulatory Assurance: Demonstrates compliance with FATF Recommendations and national AML directives.
Data Transparency: Logs and decision trails provide complete auditability.
What Is Transaction Screening?
Transaction screening focuses on analysing payment messages in real time, checking the sender, receiver, and metadata against sanctions and risk lists. It ensures that no prohibited or high-risk transactions are processed through the institution.
Key capabilities include:
Sub-Second Matching: Detects risks within milliseconds for instant payment environments like SEPA or SWIFT.
Customisable Rules: Adapts to message formats (MT/MX, ISO 20022) and institution-specific risk policies.
Dynamic Routing: Applies hold, release, or escalation logic automatically.
Integrated APIs: Connects seamlessly with payment processors and compliance engines.
Transaction screening is crucial for real-time payment compliance, fraud prevention, and transaction monitoring accuracy.
Benefits of Transaction Screening
Transaction screening delivers real-time protection at the payment level, enabling institutions to detect threats the moment a transaction is initiated. By analysing message data for sanctions, high-risk indicators, or unusual patterns, it prevents prohibited payments from being processed and supports continuous regulatory compliance.
This ensures operational speed without compromising risk management or accuracy;
Instant Compliance: Blocks or flags transactions before settlement.
Reduced Risk Exposure: Identifies threats at the point of execution.
Scalable Performance: Handles millions of transactions per second.
Regulatory Alignment: Supports continuous compliance with OFAC, EU, and UN regimes.
Key Differences
Although both involve screening against watchlists, their scope, timing, and data inputs differ significantly.
How They Work Together
Customer screening and transaction screening form complementary layers of financial crime prevention. Customer screening validates identities and profiles, while transaction screening monitors the movement of funds.
Integrating both ensures:
Continuous Risk Awareness: Each transaction is evaluated in the context of the customer’s overall profile.
Real-Time Controls: Payment screening blocks suspicious activity before settlement.
Data Feedback Loops: Screening results feed into list and threshold refinement through alert adjudication.
Benefits of Integration
When institutions combine customer and transaction screening workflows, they achieve:
Lower operational costs through unified data management.
Improved detection accuracy via consistent watchlist inputs.
Faster alert handling with shared adjudication logic.
Stronger audit trails for both KYC and payments compliance.
Integrated compliance solutions such as Facctum’s unified platform provide seamless communication between systems, ensuring transparency, scalability, and efficiency across screening processes.
External Regulatory Context
Regulatory bodies like the IMF, OFSI, and FATF emphasise that institutions must apply screening controls both at customer onboarding and transaction execution. These dual-layer defences help detect, prevent, and report suspicious activities effectively.
Summary
Customer screening and transaction screening each play a vital role in AML compliance. Customer screening ensures the right individuals enter the financial system, while transaction screening safeguards against illicit payments. Together, they create an adaptive, real-time compliance framework that balances speed, accuracy, and regulatory integrity.




